Cyber Insurance: What to know when applying for (or renewing) coverage

With businesses dominated by technology and interconnectedness, the pervasive threat of cybercrime has become larger–and costlier– than ever before. By the end of the year, the total cost of cybercrime is predicted by Cybersecurity Ventures to reach $9.5 trillion globally.
Organizations of all industries and sizes now face an increasing risk of falling victim to a cyberattack—wreaking havoc on operations, finances, and reputation. To mitigate such risk, many companies have turned to cyber insurance as a safety net, as it provides financial protection in the event of an incident.
However, as the world witnesses a staggering surge in cybercrime and its associated costs, obtaining comprehensive and affordable cyber insurance coverage has turned into an uphill battle. Let’s identify the reasons why cyber insurance is becoming harder to obtain for organizations, exploring the intricate relationship between the escalating cybercrime landscape and the tightening grip on cyber insurance availability.
Why is it so difficult to obtain cyber insurance coverage in 2024?
- The Frequency of Cybercrime
The first trend exacerbating the challenges organizations face in obtaining cyber insurance coverage is the relentless surge in cybercrime rates. Cybercriminals are constantly refining their techniques, now leveraging sophisticated tactics such as ransomware and social engineering scams.
This escalating threat landscape has resulted in a higher likelihood of successful cyberattacks, leading insurers to reassess their risk models and become more stringent in their underwriting processes. Over the past three years, cyber insurance claims have increased 100%, while insurance payouts have increased 200%. As a result, organizations are finding it increasingly difficult to meet the stringent criteria set by insurers, particularly if they operate in high-risk industries or lack robust cybersecurity measures.
While no organization is immune to cybercrime, insurers may ask applicants and policyholders to provide more information about the impact of an incident or demonstrate progress against a certain control over time. Collecting evidence is a time-consuming, resource-draining process, and the absence of a universal underwriting policy can make it even more frustrating when applying for or renewing cyber insurance.
- Rising Costs of Cyber Incidents
Another significant trend impacting cyber insurance availability is the mounting costs associated with cyber incidents. Financial fallout from a single cyberattack can be staggering, encompassing expenses related to incident response, data recovery, legal actions, reputational damage, regulatory fines, and potential lawsuits. This holds especially true for the U.S.-based companies specifically, as the average total cost of a data breach in the United States climbed to $9.48 million in 2023.
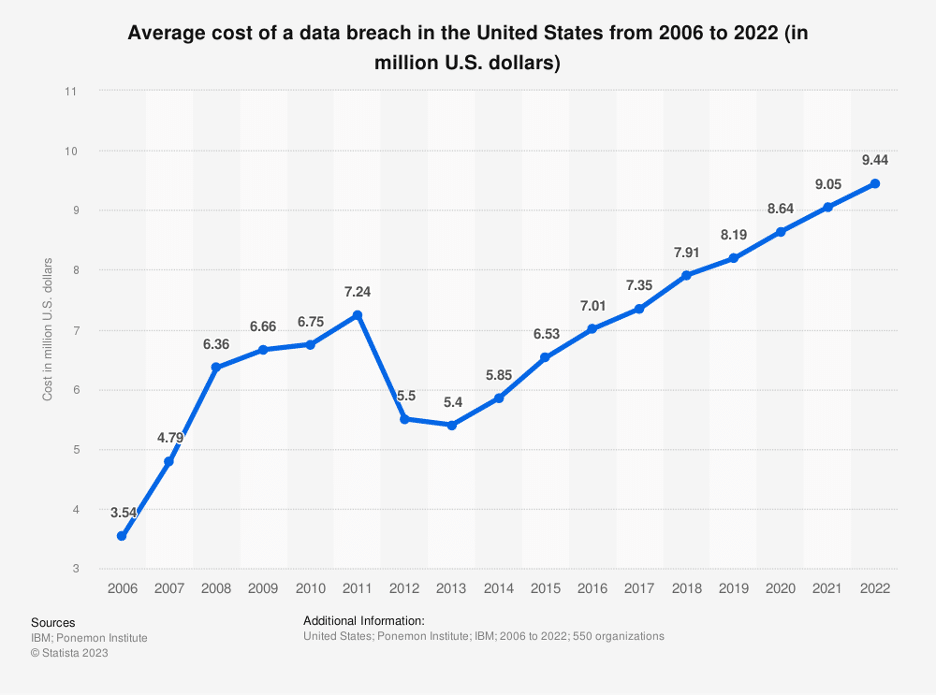
Insurers are acutely aware of the potential financial liabilities and are consequently adjusting their premiums and coverage terms accordingly. Organizations that have experienced previous cyber incidents or lack the necessary cybersecurity protocols may find themselves facing exorbitant insurance costs or even outright denial of coverage.
- Limited Historical Data
The evolving nature of cyber threats presents a unique challenge for insurers in accurately assessing risks and setting appropriate coverage terms. Unlike other forms of insurance where historical data plays a significant role in determining risk, the rapidly evolving nature of cybercrime makes it difficult to predict future attack vectors and their potential impact.
Insurers face difficulties in accurately assessing an organization’s cyber risk profile, especially for emerging threats or vulnerabilities that have not yet manifested on a large scale. This limited historical data makes it harder for organizations to demonstrate their risk mitigation strategies and secure favorable cyber insurance coverage.
How can organizations improve their chances of obtaining cyber insurance coverage?
Insurance companies assess an organization’s cyber risk profile by considering various factors, including their history of security incidents, proactive cybersecurity measures, and the nature of their operations. However, assessing emerging threats or vulnerabilities lacking extensive historical data poses a challenge. Insurers may employ specialized risk assessment tools, collaborate with cybersecurity experts, and analyze industry trends to evaluate potential risks. Additionally, insurers may emphasize the importance of proactive measures, such as implementing robust cybersecurity controls and staying informed about emerging threats, to mitigate uncertainties associated with limited historical data.
While many carriers consider an organization’s history of security incidents when determining insurability, it’s not an end-all be-all for those that have previously suffered a breach.
Organizations can improve their insurability and enhance their chances of obtaining comprehensive and affordable cyber insurance coverage by taking proactive steps to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. There are 12 primary controls that are also weighted heavily during the cyber application review process.
Organizations should consider proactively enforcing these controls prior to applying for or renewing their policy, which include:
- Multi-factor authentication for remote access and privileged controls
- Email filtering and web security,
- Secured backups,
- Privileged access management
- Endpoint detection and response
- Patch and vulnerability management
- Cyber incident response planning
- Cybersecurity awareness training
- Hardening techniques
- Logging and monitoring
- End-of-life systems replacement, and
- Vendor and digital supply chain risk management.
Although obtaining comprehensive and affordable cyber insurance coverage has become increasingly challenging in recent years, businesses must remain vigilant, implement robust cybersecurity measures, and work closely with insurers to navigate the complex world of cyber insurance.
Noetic can help organizations implement, enforce, and collect evidence of robust cybersecurity controls and policies. Learn more about Noetic for cyber insurance applications and renewals.
