The CMDB and its role in IT Asset Management

Maintaining order amidst the chaos of ever-evolving technologies can be an overwhelming challenge. With countless devices, applications, and interdependencies to manage, organizations require a robust solution to keep track of their IT assets, configurations, and relationships. This is where the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) steps in as a vital asset to empower businesses in taming the complexity of their IT environments.
What is a CMDB?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is defined as a centralized repository that stores information about an organization’s IT assets, their configurations, and–to an extent–the relationships between them. From hardware devices and software applications to network connections and service relationships, a CMDB houses a treasure trove of data that provides the foundation for effective IT asset management (ITAM).
Each CMDB is comprised of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s IT assets. Essential components of a CMDB include configuration items (CIs), relationships, and attributes and attribute sets.
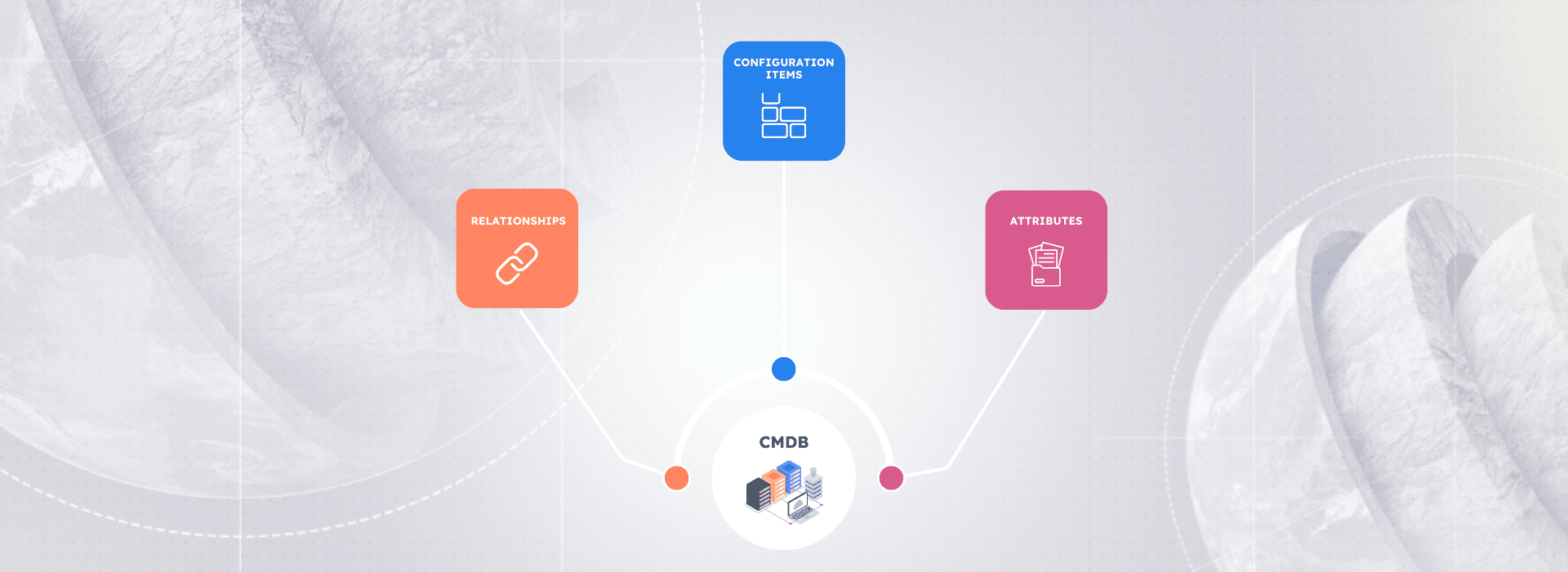
- Configuration Items (CIs)
Configuration Items are the building blocks of a CMDB. They represent individual assets within an organization’s IT infrastructure, such as servers, switches, applications, and databases. Each CI in the CMDB has unique attributes, such as a unique identifier, type, version, and relationships with other CIs. These attributes provide a detailed description of the CI and its role within the IT infrastructure.
- Relationships
Relationships define the connections and dependencies between different CIs in the CMDB. For example, a server CI may have relationships with an application CI, a database CI, and a storage CI. These relationships help establish a clear understanding of the dependencies and impact of changes. By visualizing the relationships between CIs, organizations can effectively plan changes, identify potential risks, and ensure smooth operations.
- Attributes and attribute sets
Attributes are the characteristics or properties of a CI in the CMDB. Each CI has a set of attributes that define its unique properties, such as IP address, manufacturer, model, and location. Attributes provide detailed information about a CI, enabling IT teams to make informed decisions and perform accurate impact assessments. Attribute sets group related attributes together, allowing for easier management and categorization of CIs.
The CMDB plays a crucial role in configuration management, which involves tracking and controlling changes to an organization’s assets. With a CMDB in place, organizations can establish baselines for their IT configurations, track changes, and assess the impact of those changes. This enables organizations to effectively manage and control their IT infrastructure, ensuring stability and minimizing disruptions.
Additionally, a CMDB facilitates the process of incident response. When an incident occurs, IT teams can quickly access the CMDB to identify the affected CIs, their relationships, and the potential impact on other services. This information enables IT teams to prioritize incidents, assign resources, and resolve issues promptly.
Benefits of implementing a CMDB
Implementing a CMDB can yield numerous benefits for organizations seeking to streamline their ITAM processes. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of implementing a CMDB:
1. Improved visibility and control
A CMDB offers organizations a complete and accurate view of their IT assets, configurations, and relationships. This visibility enables IT managers to understand the impact of changes, identify dependencies, and make informed decisions. With greater control over their IT infrastructure, organizations can effectively manage risks, minimize downtime, and ensure efficient service delivery.
2. Enhanced change management
Managing changes in an IT environment can be a daunting task. A CMDB provides a centralized platform to track and manage changes, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to up-to-date information. This enables organizations to assess the impact of changes, plan effectively, and minimize disruptions. By maintaining a comprehensive record of all changes, organizations can also improve auditing and compliance processes.
3. Increased efficiency and productivity
With a CMDB in place, organizations can automate routine tasks, such as asset discovery, configuration updates, and incident management. This automation saves time, reduces human error, and improves overall efficiency. Additionally, by having accurate information readily available, IT teams can respond to incidents faster, resolve issues more efficiently, and minimize the impact on end-users. This translates into increased productivity and improved service levels.
4. Elevated security practices
A CMDB helps manage user access to critical assets. By maintaining an inventory of privileged accounts and their associated permissions, security teams can better control access and proactively reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Additionally, the CMDB tracks the historical changes made to assets and configurations. Over time, this historical data can be used for trend analysis, helping organizations identify patterns of security incidents and emerging threats.
5. Regulatory compliance
Overall, the CMDB’s ability to centralize and manage IT asset information, facilitate change management processes, enforce access controls, and support reporting and auditing activities contributes significantly to ensuring regulatory compliance within organizations, particularly in highly regulated industries.
Additionally, the CMDB provides organizations with comprehensive reporting capabilities, allowing them to generate audit trails, compliance reports, and documentation of IT assets and configurations. These reports help organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and respond to audit inquiries effectively.
To maximize these benefits, however, the CMDB must remain accurate. Several software and tools are available in the market, each with its own unique features and capabilities. ServiceNow, Device42 and Cloudaware are some of the popular vendors that provide CMDB solutions.
ServiceNow CMDB is a widely used solution that offers a comprehensive set of features for IT asset management and configuration management. It provides a user-friendly interface, powerful automation capabilities, and seamless integration with other IT management modules. ServiceNow CMDB is highly customizable and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of organizations.
Device42
The Device42 is an IT infrastructure management and discovery software solution designed to help organizations gain comprehensive visibility and control over their IT assets, networks, and data center environments. Device42 offers a range of features to support IT operations, asset management, and capacity planning.
Cloudaware
The Cloudaware CMDB helps organizations gain visibility and control over their cloud-based and on-premises IT assets and configurations. It serves as a centralized repository of information about an organization’s cloud resources and related data, providing a comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure.
When selecting a CMDB solution for your organization, the most important consideration is whether the CMDB solution is compatible with the organization’s existing systems and tools. It should seamlessly integrate with your IT infrastructure, asset management systems, and other IT management modules, as the level of CMDB accuracy depends on its integrability. it should also be a resource to help the security team triage and escalate security investigations based on device ownership or criticality.
The Challenges of CMDB Implementation
Implementing and maintaining a CMDB can present various challenges for organizations, including:
- Complexity of IT Environment: Organizations often struggle with capturing and maintaining accurate information about their IT assets and configurations, particularly in complex and dynamic IT environments. To mitigate this challenge, organizations should prioritize the identification and documentation of critical assets, establish clear data governance policies, and leverage automation tools for data discovery and population.
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: Maintaining accurate and complete data within the CMDB is crucial for its effectiveness. Organizations may encounter challenges related to data quality, duplication, inconsistency, and outdated information. To address these challenges, organizations should implement data validation processes, conduct regular audits and reconciliations, and establish data stewardship roles to ensure data integrity and completeness.
- Organizational Resistance: Resistance from stakeholders, such as IT teams, business units, and senior management, can hinder the implementation and adoption of the CMDB. To overcome resistance, organizations should communicate the benefits of the CMDB effectively, involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process, provide adequate training and support, and address concerns and objections proactively.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, including budget, time, and skilled personnel, can pose challenges during the implementation and maintenance of a CMDB. To address resource constraints, organizations should prioritize activities based on their strategic importance, leverage automation and tooling to streamline processes, seek external expertise or assistance if needed, and establish realistic timelines and milestones.
By addressing these challenges proactively and implementing best practices in CMDB implementation and maintenance, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and value of their CMDB initiatives.
How Noetic Helps
Noetic leverages Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to integrate CMDB data with other IT management systems and security tools such as endpoint detection & response, vulnerability management, cloud security and more. The platform’s comprehensive asset and exposure information, relationship mapping, and impact analysis capabilities significantly enhance incident response and resolution times, ultimately contributing to improved IT service delivery and organizational resilience.
Real-world examples of these instances include:
- Service Impact Analysis: In the event of a critical incident, such as a server failure disrupting a business-critical application, the CMDB provides immediate visibility into the impacted configuration items, their relationships, and dependencies. This allows IT teams to quickly identify the root cause, assess the impact on other services, and prioritize incident response efforts. By proactively addressing the issue and allocating resources effectively, resolution times are minimized, and business continuity is maintained.
- Security Incident Response: In the event of a security breach or cyberattack, Noetic correlates security event data with CMDB information so that incident responders can quickly determine the scope of the incident, assess potential impact on critical systems, and initiate containment and remediation actions promptly. This rapid response reduces dwell time, limits the spread of the attack, and minimizes the overall impact on organizational security posture and reputation.
- Change Management: Before implementing a planned change to the network infrastructure, IT teams can leverage Noetic to perform impact analysis and assess potential risks. By analyzing relationships between network devices, applications, and services, IT teams can identify dependencies, conflicts, or vulnerabilities arising from the change. This proactive assessment enables them to implement preventive measures, communicate effectively with stakeholders, and execute the change with minimal disruption to services, thereby improving incident response and resolution times.
Join us for a live demonstration to see how the Noetic platform provides unparalleled visibility across the entire cyber asset landscape, enabling teams to enhance change management, increase tool and resource efficacy, and optimize incident response.
